Peking University, May 18, 2020: A joint research team led by Sunney Xie, Director of Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Genomics (ICG) at Peking University (PKU) has successfully identified multiple highly potent neutralizing antibodies against the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, the causative virus of the respiratory disease COVID-19, from convalescent plasma by high-throughput single-cell sequencing. Generated by human immune system, neutralizing antibodies can effectively prevent viruses from infecting cells. New results from animal studies showed that their neutralizing antibody provides a potential cure for COVID-19 as well as means for short-term prevention. This marks a major milestone in the fight against the pandemic.
This study has been published online in Cell, titled "Potent neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 identified by high-throughput single-cell sequencing of convalescent patients’ B cells ". This work was jointly conducted by Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Genomics and Biomedical Pioneering Innovation Center of Peking University, Beijing YouAn Hospital of Capital Medical University, Institute of Laboratory Animal Science (ILAS) of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Comparative Medicine Center, Peking Union Medical College, Beijing Institute of Microbiology and Epidemiology of Academy of Military Medical Sciences, Sino Biological, Inc., WuXi Biologics and Singlomics. The co-authors of this article are Yunlong Cao, Bin Su, Xianghua Guo, Wenjie Sun, Yongqiang Deng, Linlin Bao, Qinyu Zhu. The corresponding authors are Chuan Qin, Chengfeng Qin, Ronghua Jin, and Sunney Xie. The work which began on Jan. 27, 2020 was supported by The People’s Government of Beijing Municipality, the Ministry of Science and Technology and the Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China.


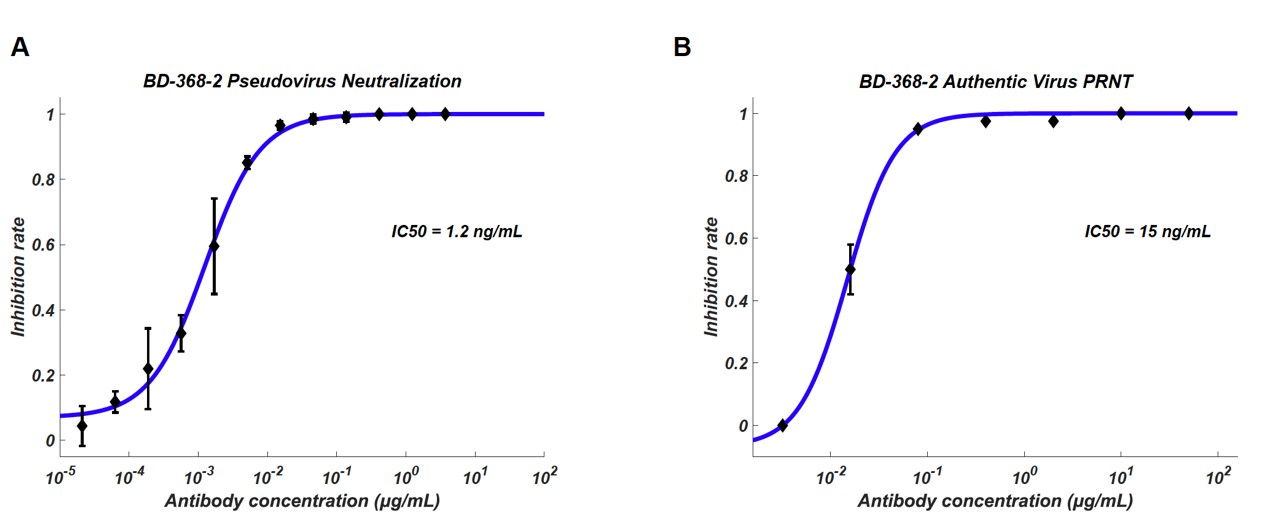
Neutralization potency of BD-368-2 antibody against pseudovirus and authentic virus, IC50 reached 8pM and 100pM respectively
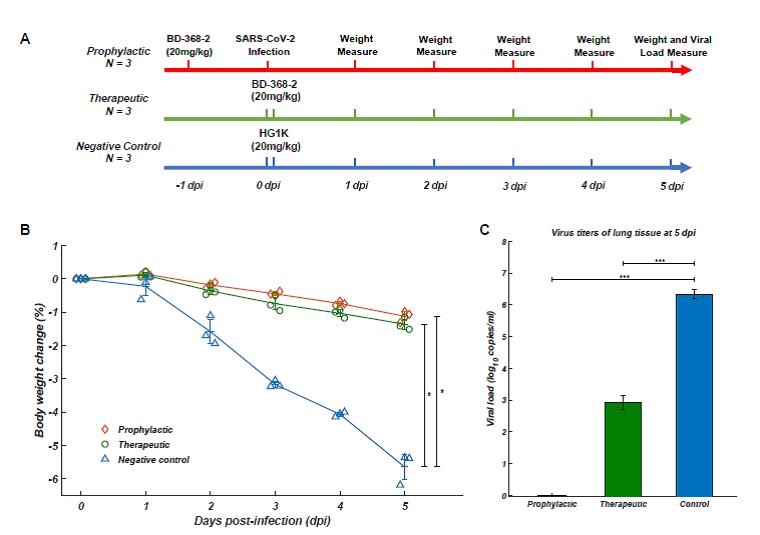
Testing on the therapeutic and prophylactic efficacy of neutralizing antibodies on mice models (A)Therapeutic group (green), injected with BD-368-2 two hours after infection (n=3); prophylactic group (red), injected with BD-368-2 one day before infection (n=3); control group (blue) injected with nonrelevant antibody two hours after infection.(B)The rate of weight loss of therapeutic and prophylactic groups was significantly lower than that of the control group.(C)After 5 days, the viral load of therapeutic group decreased by ~ 2400 times; no viral load was detected in the prophylactic group.

(A&B) Cryo-EM structure of BD-23 Fab in complex with the Spike-ectodomain trimer (C) RBD/ACE2 complex structure overlays with RBD/ BD-23 Fab structure, which demonstrates BD-23 Fab can block S protein binding with ACE2.